- business@first-powersolar.com
- The World Centre, Sen. Gil J. Puyat Ave, Makati, Metro Manila
Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, also referred to as solar voltaic systems, are renewable energy technologies that convert sunlight directly into electricity using photovoltaic cells. These systems are increasingly popular due to their environmental benefits and potential for sustainable energy production. This article explores what photovoltaic systems are, how they work, their components, effects, types, and advantages.
A photovoltaic system is a power system designed to generate electricity by converting solar energy into direct current (DC) electricity using semiconducting materials, primarily silicon, in photovoltaic cells. These systems can be deployed in various scales, from small residential setups to large utility-scale solar farms, providing clean energy for homes, businesses, and communities.
Photovoltaic systems operate based on the photovoltaic effect, where sunlight excites electrons in a semiconductor material, generating an electric current. Here’s a simplified overview of the process:
Generation of Electric Current: The absorbed energy causes electrons to move, creating a flow of electric current (DC).
Conversion to Usable Power: An inverter converts the DC electricity into alternating current (AC), suitable for household and grid use.
Distribution: The electricity is distributed to power appliances, stored in batteries, or fed into the electrical grid.
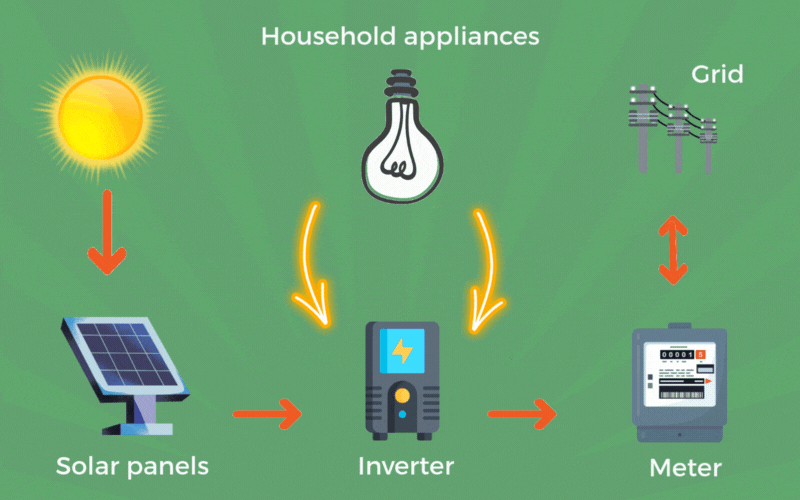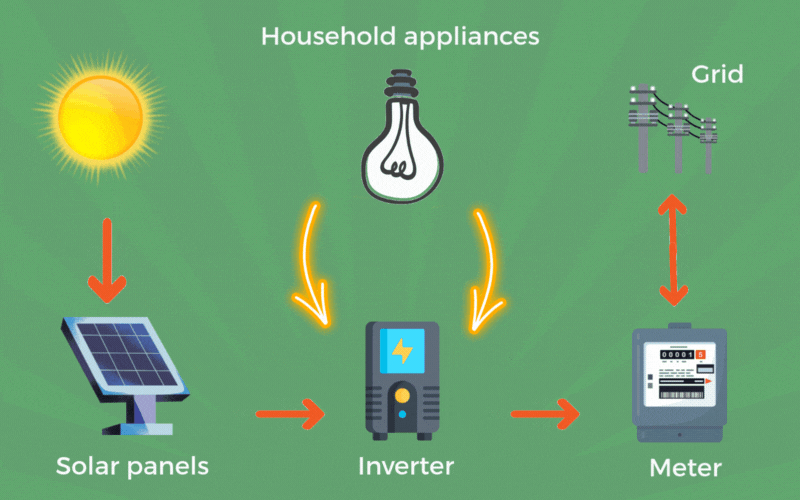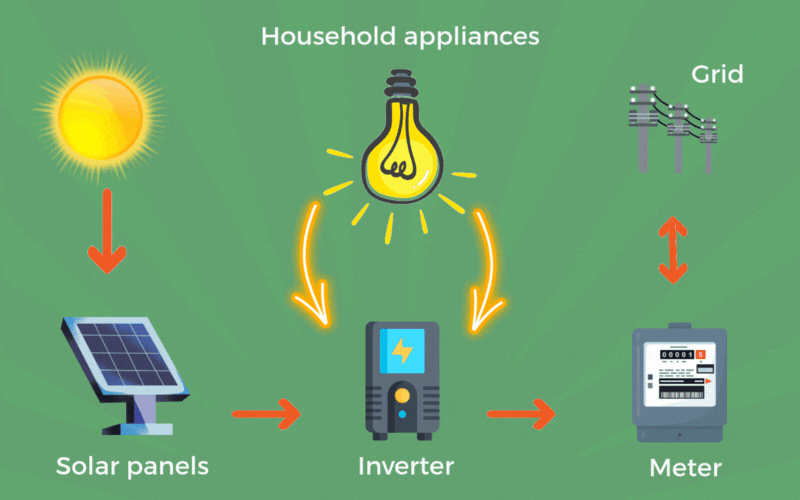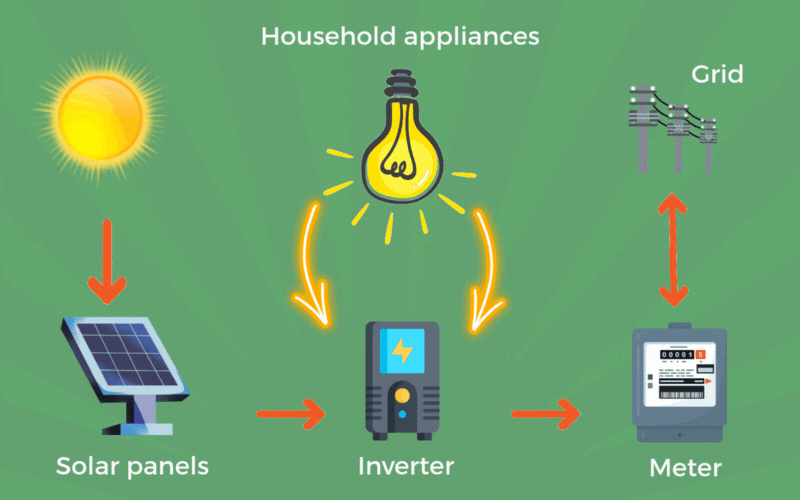
A typical PV system consists of several key components:
Photovoltaic systems have significant environmental, economic, and social impacts:
Photovoltaic systems are categorized based on their configuration and application:
Photovoltaic systems offer numerous benefits, making them a compelling choice for energy production:
Solar photovoltaic systems are a cornerstone of the transition to renewable energy, offering a sustainable, efficient, and versatile solution for electricity generation. By understanding their components, types, and benefits, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about adopting this technology. As advancements in PV technology continue, these systems will play an increasingly vital role in powering a cleaner, greener future.
Empowering a sustainable future with cutting-edge solar solutions, First Power Solar Inc. is committed to delivering reliable and efficient renewable energy for businesses
Get updates on special events, news & trends